티스토리 뷰
이동욱 님의 '스프링부트와 AWS로 혼자 구현하는 웹 서비스' 책 내용을 정리한 것입니다.
3장 스프링 부트에서 JPA로 데이터베이스 다뤄보자
SQL 생성하는 것의 문제점
- 반복적인 작업
- 패러다임 불일치: 객체를 데이터베이스에 저장하니 여러 문제 발생
⬇️ 객체 지향 프로그래밍 언어와 관계형 데이터베이스 중간에서 패러다임을 일치 시켜주기 위해!
JPA 등장
(개발자) 객체 지향적으로 프로그래밍
(JPA) 관계형 DB에 맞게 SQL 대신 생성해서 실행
JPA
- 인터페이스 (사용하려면 구현체 필요)
- JPA ← Hibernate ← Spring Data JPA
- 자바 표준명세서
Spring Data JPA 등장 이유
- 구현체 교체 용이
- 저장소 교체 용이
요구사항 분석
1. 게시판 기능
▶️ 게시글 조회, 등록, 수정, 삭제
2. 회원 기능
▶️ 구글 / 네이버 로그인
▶️ 로그인한 사용자 글 작성 권한
▶️ 본인 작성 글에 대한 권한 관리
build.gradle - 프로젝트에 Spring Data JPA, H2 데이터베이스 적용
implementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-data-jpa'
implementation 'com.h2database:h2'
Spring Data JPA
- 스프링 버전에 맞춰서 자동으로 JPA 관련 라이브러리 버전 관리
H2 데이터베이스
- 인메모리 관계형 데이터베이스
- 메모리에서 실행 → 재시작할 시 초기화 → 테스트 용도로 사용
Posts.java - 실제 DB의 테이블과 매칭될 클래스
package com.example.project.domain.posts;
import jakarta.persistence.*;
import lombok.Builder;
import lombok.Getter;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
@Getter
@NoArgsConstructor
@Entity
public class Posts {
@Id // PK
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Long id;
@Column(length = 500, nullable = false)
private String title;
@Column(columnDefinition = "TEXT", nullable = false)
private String content;
private String author;
@Builder
public Posts(String title, String content, String author) {
this.title = title;
this.content = content;
this.author = author;
}
}
<JPA에서 제공하는 어노테이션>
- @Entity
- 테이블과 링크될 클래스임을 나타냄
- 기본값으로 클래스의 카멜케이스 이름을 _(언더스코어)로 매칭
- @Id
- 해당 테이블의 PK
- @GeneratedValue
- PK의 생성 규칙
- @Column
- 선언 안해도 해당 클래스의 필드는 모두 칼럼이 됨
- 기본값 외 추가 변경이 필요한 옵션이 있을 경우 사용
<롬복에서 제공하는 어노테이션>
- @NoArgsConstructor
- 기본 생성자 자동 추가
- @Getter
- 클래스 내 모든 필드 getter 메소드 자동 생성
- @Builder
- 해당 클래스의 빌더 패턴 클래스 생성
- 생성자 상단에 선언 시 생성자에 포함된 필드만 빌더에 포함
Entity 클래스에서 절대 Setter 메서드를 만들지 ❌
🤔 Setter가 없는 상황에서 어떻게 값을 채워 DB에 삽입할까? ➡️ 생성자를 통해 최종값을 채운 후 DB에 삽입
PostsRepository.java
package com.example.project.domain.posts;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
public interface PostsRepository extends JpaRepository<Posts, Long> {
}- JpaRepository<Entity 클래스, PK 타입> 상속하면 기본적인 CRUD 메서드가 자동 생성
- @Repository 추가 필요 없음
- Entity 클래스와 기본 Entity Repository 함께 위치
PostsRepositoryTest.java
package com.example.project.posts;
import com.example.project.domain.posts.Posts;
import com.example.project.domain.posts.PostsRepository;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.After;
import org.assertj.core.api.Assertions;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.extension.ExtendWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit.jupiter.SpringExtension;
import java.util.List;
@ExtendWith(SpringExtension.class)
@SpringBootTest
public class PostsRepositoryTest {
@Autowired
PostsRepository postsRepository;
@After("")
public void cleanup() {
postsRepository.deleteAll();
}
@Test
public void 게시글저장_불러오기() {
// given
String title = "테스트 게시글";
String content = "테스트 본문";
postsRepository.save(Posts.builder()
.title(title)
.content(content)
.author("yuma@gmail.com")
.build());
// when
List<Posts> postsList = postsRepository.findAll();
// then
Posts posts = postsList.get(0);
Assertions.assertThat(posts.getTitle()).isEqualTo(title);
Assertions.assertThat(posts.getContent()).isEqualTo(content);
}
}@After
- JUnit 단위 테스트가 끝날 때마다 수행되는 메소드
- 여러 테스트 동시에 수행 시 H2에 데이터가 그대로 남아 있어 다음 테스트 실행 시 테스트 실패할 가능성 있음
postsRepository.save
- 테이블 posts에 insert/update 쿼리 실행
- id가 있으면 update, 없다면 insert 쿼리 실행
postsRepository.findAll
- 테이블 posts에 있는 모든 데이터 조회
application.properties - 실제 실행된 쿼리 확인하기 위한 코드 추가
spring.jpa.show-sql=true
⭐️ API 만들 때 필요한 것 ⭐️
1. Request 데이터 받을 Dto
2. API 요청 받을 Controller
3. 트랜잭션, 도메인 기능 간의 순서를 보장하는 Service
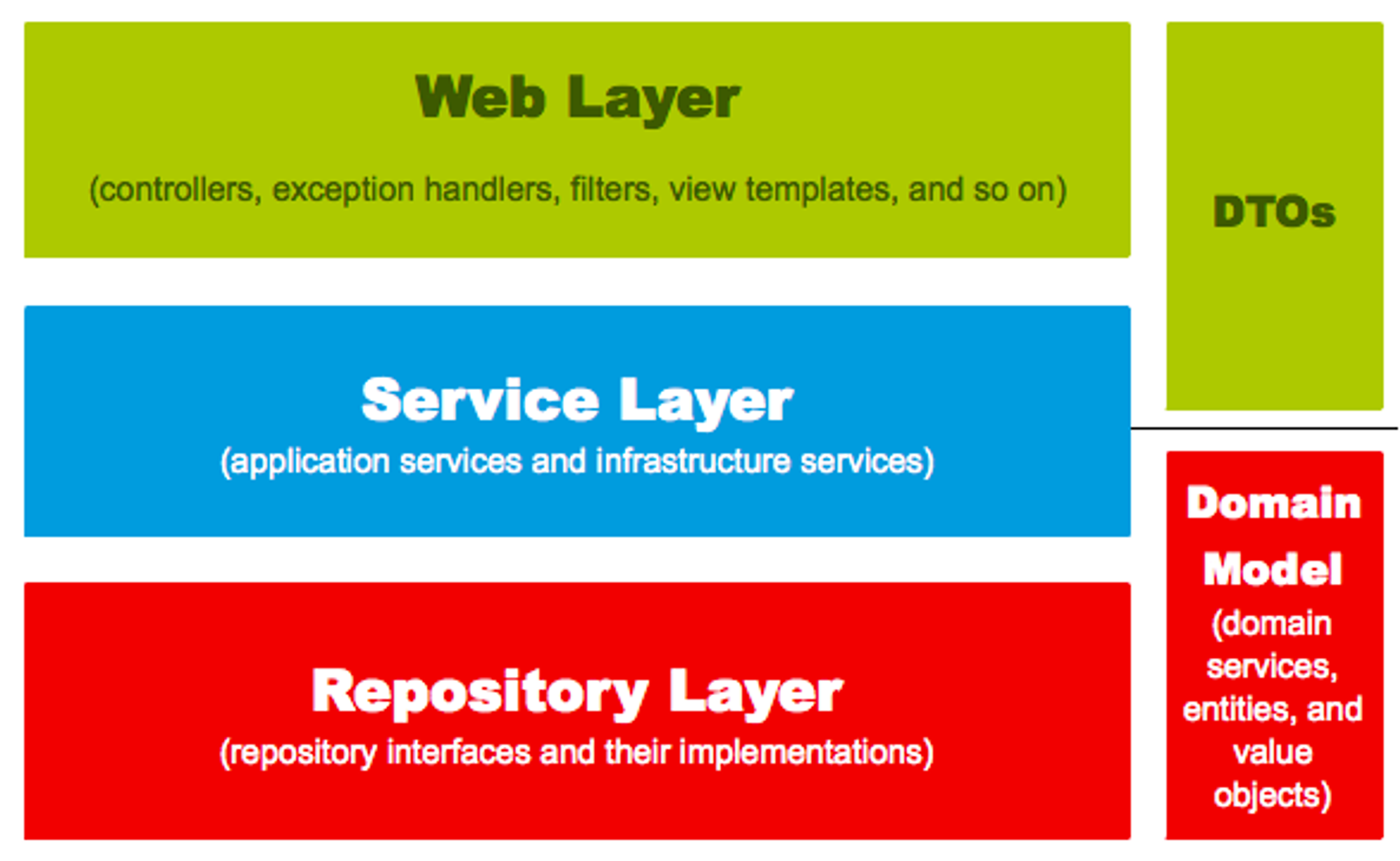
Web Layer
- 컨트롤러, JSP/Freemarker 뷰 템플릿 영역
- 외부 요청과 응답에 대한 전반적인 영역
Service Layer
- @Service에 사용
- Controller와 Dao의 중간 영역
- @Transactional이 사용되어야 하는 영역
Repository Layer
- 데이터 저장소에 접근
Dtos
- Dto가 계층 간에 데이터 교환을 위한 객체, Dtos가 Dto 영역
Domain Model
- 도메인이라 불리는 개발 대상을 모든 사람이 동일한 관점에서 이해할 수 있고 공유할 수 있도록 단순화시킨 것
이 5가지 Layer에서 비지니스 처리를 담당해야 할 곳은? "Domain"
▶️ 로직이 서비스 클래스 내부에서 처리될 경우, 서비스 계층이 무의미해지며 객체란 단순히 데이터 덩어리 역할만 하게 됨
▶️ 도메인 모델로 처리할 경우, 서비스 클래스에서는 트랜잭션과 도메인 간의 순서만 보장
PostsApiController.java
package com.example.project.web;
import com.example.project.service.posts.PostsService;
import com.example.project.web.dto.PostsSaveRequestDto;
import lombok.RequiredArgsConstructor;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RequiredArgsConstructor
@RestController
public class PostsApiController {
private final PostsService postsService;
@PostMapping("/api/v1/posts")
public Long save(@RequestBody PostsSaveRequestDto requestDto) {
return postsService.save(requestDto);
}
}
PostsService.java
package com.example.project.service.posts;
import com.example.project.domain.posts.PostsRepository;
import com.example.project.web.dto.PostsSaveRequestDto;
import lombok.RequiredArgsConstructor;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
@RequiredArgsConstructor
@Service
public class PostsService {
private final PostsRepository postsRepository;
@Transactional
public Long save(PostsSaveRequestDto requestDto) {
return postsRepository.save(requestDto.toEntity()).getId();
}
}
@RequiredArgsConstructor
final이 선언된 모든 필드를 인자값으로 하는 생성자를 대신 생성
<스프링에서 Bean을 주입받는 방식>
1. @Autowired
2. setter
3. 생성자 (권장)
PostsSaveRequestDto.java
package com.example.project.web.dto;
import com.example.project.domain.posts.Posts;
import lombok.Builder;
import lombok.Getter;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
@Getter
@NoArgsConstructor
public class PostsSaveRequestDto {
private String title;
private String content;
private String author;
@Builder
public PostsSaveRequestDto(String title, String content, String author) {
this.title = title;
this.content = content;
this.author = author;
}
public Posts toEntity() {
return Posts.builder()
.title(title)
.content(content)
.author(author)
.build();
}
}
Entity 클래스를 Request/Response 클래스로 사용 ❌
▶️ Entity 클래스는 DB와 맞닿은 핵심 클래스이므로 이 클래스를 기준으로 생성 및 변경한다. Entity 클래스가 변경되면 여러 클래스에 영향을 끼치지만 Request와 Response용 Dto는 View를 위한 클래스라 자주 변경이 필요하다.
⭐️ View Layer와 DB Layer 분리 필요!
PostsApiControllerTest.java
package com.example.project.web;
import com.example.project.domain.posts.Posts;
import com.example.project.domain.posts.PostsRepository;
import com.example.project.web.dto.PostsSaveRequestDto;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.After;
import org.assertj.core.api.Assertions;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.extension.ExtendWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.boot.test.web.client.TestRestTemplate;
import org.springframework.boot.test.web.server.LocalServerPort;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit.jupiter.SpringExtension;
import java.util.List;
@ExtendWith(SpringExtension.class)
@SpringBootTest(webEnvironment = SpringBootTest.WebEnvironment.RANDOM_PORT)
public class PostsApiControllerTest {
@LocalServerPort
private int port;
@Autowired
private TestRestTemplate restTemplate;
@Autowired
private PostsRepository postsRepository;
@After("")
public void tearDown() throws Exception {
postsRepository.deleteAll();
}
@Test
public void Posts_등록된다() throws Exception {
// given
String title = "title";
String content = "content";
PostsSaveRequestDto requestDto = PostsSaveRequestDto.builder()
.title(title)
.content(content)
.author("author")
.build();
String url = "http://localhost:" + port + "/api/v1/posts";
// when
ResponseEntity<Long> responseEntity = restTemplate.postForEntity(url, requestDto, Long.class);
//then
Assertions.assertThat(responseEntity.getStatusCode()).isEqualTo(HttpStatus.OK);
Assertions.assertThat(responseEntity.getBody()).isGreaterThan(0L);
List<Posts> all = postsRepository.findAll();
Assertions.assertThat(all.get(0).getTitle()).isEqualTo(title);
Assertions.assertThat(all.get(0).getContent()).isEqualTo(content);
}
}@WebMvcTest
- JPA 기능이 작동하지 ❌
@SpringBootTest
- JPA 기능까지 한번에 테스트할 때
-- 여기까지가 게시글 등록 기능! 다음은 수정, 조회 기능 --
PostsApiController.java
package com.example.project.web;
import com.example.project.service.posts.PostsService;
import com.example.project.web.dto.PostsResponseDto;
import com.example.project.web.dto.PostsSaveRequestDto;
import com.example.project.web.dto.PostsUpdateRequestDto;
import lombok.RequiredArgsConstructor;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
@RequiredArgsConstructor
@RestController
public class PostsApiController {
private final PostsService postsService;
// 게시글 등록
@PostMapping("/api/v1/posts")
public Long save(@RequestBody PostsSaveRequestDto requestDto) {
return postsService.save(requestDto);
}
// 게시글 수정
@PutMapping("/api/v1/posts/{id}")
public Long update(@PathVariable Long id, @RequestBody PostsUpdateRequestDto requestDto) {
return postsService.update(id, requestDto);
}
// 게시글 조회
@GetMapping("/api/v1/posts/{id}")
public PostsResponseDto findById(@PathVariable Long id) {
return postsService.findById(id);
}
}
PostsResponseDto.java
package com.example.project.web.dto;
import com.example.project.domain.posts.Posts;
import lombok.Getter;
@Getter
public class PostsResponseDto {
private Long id;
private String title;
private String content;
private String author;
public PostsResponseDto(Posts entity) {
this.id = entity.getId();
this.title = entity.getTitle();
this.content = entity.getContent();
this.author = entity.getAuthor();
}
}→ Entity 필드 중 일부만 사용
PostsUpdateRequestDto.java
package com.example.project.web.dto;
import lombok.Builder;
import lombok.Getter;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
@Getter
@NoArgsConstructor
public class PostsUpdateRequestDto {
private String title;
private String content;
@Builder
public PostsUpdateRequestDto(String title, String content) {
this.title = title;
this.content = content;
}
}
Posts.java
package com.example.project.domain.posts;
import com.example.project.domain.BaseTimeEntity;
import jakarta.persistence.*;
import lombok.Builder;
import lombok.Getter;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
@Getter
@NoArgsConstructor
@Entity
public class Posts extends BaseTimeEntity {
@Id // PK
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Long id;
@Column(length = 500, nullable = false)
private String title;
@Column(columnDefinition = "TEXT", nullable = false)
private String content;
private String author;
@Builder
public Posts(String title, String content, String author) {
this.title = title;
this.content = content;
this.author = author;
}
public void update(String title, String content) {
this.title = title;
this.content = content;
}
}→ update 메서드 추가
PostsService.java
package com.example.project.service.posts;
import com.example.project.domain.posts.Posts;
import com.example.project.domain.posts.PostsRepository;
import com.example.project.web.dto.PostsResponseDto;
import com.example.project.web.dto.PostsSaveRequestDto;
import com.example.project.web.dto.PostsUpdateRequestDto;
import lombok.RequiredArgsConstructor;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
@RequiredArgsConstructor
@Service
public class PostsService {
private final PostsRepository postsRepository;
// 게시글 등록
@Transactional
public Long save(PostsSaveRequestDto requestDto) {
return postsRepository.save(requestDto.toEntity()).getId();
}
// 게시글 수정
@Transactional
public Long update(Long id, PostsUpdateRequestDto requestDto) {
Posts posts = postsRepository.findById(id)
.orElseThrow(() -> new IllegalArgumentException("해당 게시글이 없습니다. id = " + id));
posts.update(requestDto.getTitle(), requestDto.getContent());
return id;
}
// 게시글 조회
public PostsResponseDto findById(Long id) {
Posts entity = postsRepository.findById(id)
.orElseThrow(() -> new IllegalArgumentException("해당 게시글이 없습니다. id = " + id));
return new PostsResponseDto(entity);
}
}JPA 영속성 컨텍스트 때문에 쿼리 날리는 부분이 없음!
영속성 컨텍스트: Entity를 영구 저장하는 환경
PostsApiControllerTest.java
package com.example.project.web;
import com.example.project.domain.posts.Posts;
import com.example.project.domain.posts.PostsRepository;
import com.example.project.web.dto.PostsSaveRequestDto;
import com.example.project.web.dto.PostsUpdateRequestDto;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.After;
import org.assertj.core.api.Assertions;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.extension.ExtendWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.boot.test.web.client.TestRestTemplate;
import org.springframework.boot.test.web.server.LocalServerPort;
import org.springframework.http.HttpEntity;
import org.springframework.http.HttpMethod;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit.jupiter.SpringExtension;
import java.util.List;
@ExtendWith(SpringExtension.class)
@SpringBootTest(webEnvironment = SpringBootTest.WebEnvironment.RANDOM_PORT)
public class PostsApiControllerTest {
@LocalServerPort
private int port;
@Autowired
private TestRestTemplate restTemplate;
@Autowired
private PostsRepository postsRepository;
@After("")
public void tearDown() throws Exception {
postsRepository.deleteAll();
}
@Test
public void Posts_등록된다() throws Exception {
// given
String title = "title";
String content = "content";
PostsSaveRequestDto requestDto = PostsSaveRequestDto.builder()
.title(title)
.content(content)
.author("author")
.build();
String url = "http://localhost:" + port + "/api/v1/posts";
// when
ResponseEntity<Long> responseEntity = restTemplate.postForEntity(url, requestDto, Long.class);
//then
Assertions.assertThat(responseEntity.getStatusCode()).isEqualTo(HttpStatus.OK);
Assertions.assertThat(responseEntity.getBody()).isGreaterThan(0L);
List<Posts> all = postsRepository.findAll();
Assertions.assertThat(all.get(0).getTitle()).isEqualTo(title);
Assertions.assertThat(all.get(0).getContent()).isEqualTo(content);
}
@Test
public void Posts_수정된다() throws Exception {
// given
Posts savedPosts = postsRepository.save(Posts.builder()
.title("title")
.content("content")
.author("author")
.build());
Long updateId = savedPosts.getId();
String expectedTitle = "title2";
String expectedContent = "content2";
PostsUpdateRequestDto requestDto = PostsUpdateRequestDto.builder()
.title(expectedTitle)
.content(expectedContent)
.build();
String url = "http://localhost:" + port + "/api/v1/posts/" + updateId;
HttpEntity<PostsUpdateRequestDto> requestEntity = new HttpEntity<>(requestDto);
// when
ResponseEntity<Long> responseEntity = restTemplate.exchange(url, HttpMethod.PUT, requestEntity, Long.class);
// then
Assertions.assertThat(responseEntity.getStatusCode()).isEqualTo(HttpStatus.OK);
Assertions.assertThat(responseEntity.getBody()).isGreaterThan(0L);
List<Posts> all = postsRepository.findAll();
Assertions.assertThat(all.get(0).getTitle()).isEqualTo(expectedTitle);
Assertions.assertThat(all.get(0).getContent()).isEqualTo(expectedContent);
}
}
조회 기능은 톰캣 실행해서 확인할꺼임!
application.properties
spring.jpa.show-sql=true
spring.h2.console.enabled=true
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:h2:mem:testdb
insert into posts (author, content, title) values (’author’, ‘content’, ‘title’); 쿼리 실행

Entity의 데이터 생성/수정 시간을 JPA Auditing 사용
BaseTimeEntity.java
package com.example.project.domain;
import jakarta.persistence.EntityListeners;
import jakarta.persistence.MappedSuperclass;
import lombok.Getter;
import org.springframework.data.annotation.CreatedDate;
import org.springframework.data.annotation.LastModifiedDate;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.domain.support.AuditingEntityListener;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
@Getter
@MappedSuperclass
@EntityListeners(AuditingEntityListener.class)
public class BaseTimeEntity {
@CreatedDate
private LocalDateTime createdDate;
@LastModifiedDate
private LocalDateTime modifiedDate;
}→ 모든 상위 Entity 클래스가 되어서 Entity들의 생성 시간과 수정 시간을 자동으로 관리하는 역할
@MappedSuperclass
- JPA Entity들이 BaseTimeEntity를 상속할 경우 createdDate, modifiedDate도 칼럼으로 인식
@EntityListeners(AuditingEntityListener.class)
- Auditing 기능 포함
@CreatedDate
- Entity가 생성되어 저장될 때 시간이 자동 저장
@LastModifiedDate
- Entity 값 변경할 때 시간 자동 저장
Posts.java - BaseTimeEntity 상속 받도록 변경
public class Posts extends BaseTimeEntity {
ProjectApplication.java - Auditing 기능 사용하도록 설정
@EnableJpaAuditing // JPA Auditing 활성화
PostsRepositoryTest.java - Auditing 테스트
package com.example.project.posts;
import com.example.project.domain.posts.Posts;
import com.example.project.domain.posts.PostsRepository;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.After;
import org.assertj.core.api.Assertions;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.extension.ExtendWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit.jupiter.SpringExtension;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.util.List;
@ExtendWith(SpringExtension.class)
@SpringBootTest
public class PostsRepositoryTest {
@Autowired
PostsRepository postsRepository;
@After("")
public void cleanup() {
postsRepository.deleteAll();
}
@Test
public void 게시글저장_불러오기() {
// given
String title = "테스트 게시글";
String content = "테스트 본문";
postsRepository.save(Posts.builder()
.title(title)
.content(content)
.author("yuma@gmail.com")
.build());
// when
List<Posts> postsList = postsRepository.findAll();
// then
Posts posts = postsList.get(0);
Assertions.assertThat(posts.getTitle()).isEqualTo(title);
Assertions.assertThat(posts.getContent()).isEqualTo(content);
}
@Test
public void BaseTimeEntity_등록() {
// given
LocalDateTime now = LocalDateTime.of(2019,6,4,0,0,0);
postsRepository.save(Posts.builder()
.title("title")
.content("content")
.author("author")
.build());
// when
List<Posts> postsList = postsRepository.findAll();
// then
Posts posts = postsList.get(0);
System.out.println(">>> createDate = " + posts.getCreatedDate() + ", modifiedDate = " + posts.getModifiedDate());
Assertions.assertThat(posts.getCreatedDate()).isAfter(now);
Assertions.assertThat(posts.getModifiedDate()).isAfter(now);
}
}'Spring' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Spring Cloud로 개발하는 마이크로서비스 애플리케이션(MSA) #4 (0) | 2023.07.28 |
|---|---|
| 스프링부트와 AWS로 혼자 구현하는 웹 서비스 4장 (0) | 2023.07.16 |
| 스프링부트와 AWS로 혼자 구현하는 웹 서비스 1,2장 (0) | 2023.05.25 |
| 스프링 입문 강의 정리 #6 (0) | 2023.05.22 |
| 스프링 입문 강의 정리 #5 (0) | 2023.04.18 |
